Theme: Engineering Biomolecules for Advancement of Drug Discovery and Molecular Therapeutics
Cell Biology 2020
ME Conferences invites all the participants from all over the World to attend International Conference on Cell Biology and Genomics which is going to be held during June 13-14, 2019 in Helsinki, Finland. The theme of the conference is “Engineering biomolecules for advancement of Drug discovery and Molecular therapeutics”.
Cell Biology 2019 Conference includes Oral talks, Poster presentations, and Keynote presentations, Workshops, Exhibitions, and Symposia. The conference invites the academicians, Scientists from top Universities, Researchers, Health care professionals, Biomedical Scientists, Industries, Business delegates, Young researchers and Students over the globe providing a better platform, where they can show their contributions and novel researchers in the field of Cell Biology and Genomics.
Why to attend?
The conference Cell Biology 2019 will focus on molecular-based studies like Cell and Immunology, Cell Physiology and Biochemistry, Molecular Cell Biology, Structural & Functional Genomics, Cancer Genomics, Stem Cells & Tissue Engineering. Cell Biology 2019 invites you for plenary talks, Symposium, workshops, invited sessions, oral and poster sessions from various universities and associations. This conference will help to meet personalities in the field of Cell Biology and Genomics to learn the latest technological advancements.
Target Audience:
Our organization would be privileged to welcome
- Molecular Therapists
- Cell Biologists
- Stem cell Researchers
- Molecular Biologists
- Molecular Researchers
- Academicians
- Molecular Medicine Associations and Societies
- Post-Doctoral fellows
- Scientists
- Young Researchers
- Delegates from Pharmaceutical industries
- Students and many more…
Track 1: Cell and Immunology
The cell is the basic structural, biological and functional unit of all known living organisms and it is the smallest unit of life. Cells are the study of building blocks of life.T he human body is collected of trillions of cells they provide structure for the body take in nutrients from food transform those nutrients into energy and carry out specialized functions. The cells die through infection, poisoning, overheating or lack of oxygen. Immunology is important in medical and biological sciences also it protects us from infection through various lines of defense. As it should, it is not functioning of immune system and it can result in diseases such as autoimmunity, Cancer Cell, and allergy. When health conditions aggravate to emergency status, portions of immune system organs including the thymus, spleen, bone marrow, lymph nodes, and other lymphatic tissues can be surgically excised for consideration while patients are still alive.Immunological memory refers to the capacity of the immune system to respond more compact to successive exposures to the same antigen.
Track 2: Cellular Metabolism & Signaling
Cell Signaling is part of any communication process that governs coordinates all cell and basic activities of cells actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, immunity and tissue repair as well as normal tissue homeostasis. On studying individual parts of cell signaling pathways has focused on Traditional Work. Transport System biology research helps us to understand the underlying structure of cell signaling networks and how changes in these networks may affect the flow and transmission of information. Modeling and Simulations analysis of cell signaling networks requires a combination of experimental and theoretical approaches including the analysis and development. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are characterized by their ability to either break down of complex molecule biology by releasing energy in the process or structure of molecules with the utilization of energy. The Energy is released from two pathways complement each other in that from one is used up by the other.
Track 3: Membrane Processes
Selective barrier and it allows some things to pass through but stops others such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles are called Membrane. The uses of Membrane covers all engineering approaches for with the help of permeable membranes the transport of substances between two fractions. In prevalent, mechanical separation processes for separating gaseous or liquid streams use membrane technology. There are four types of membrane filtration process classifications are Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, and Reverse osmosis. Membrane biochemistry processes cover a group of separation processes in which the characteristics of a membrane (porosity, selectivity, electric charge) are used to separate the components of a suspension or a solution. In these processes, the feed stream is split into two, the fraction that permeates through the membrane called the Permeate and the fraction containing the components that have not been transported through the membrane usually called the Retentate. The size of the components to be separated and magnitude and the nature of the driving force provide criteria for a classification of the membrane separation processes. It should be noted that the boundaries between some of the processes, such as Ultrafiltration and Reverse osmosis are arbitrary.
Track 4: Cell Physiology and Biochemistry
Cell physiology is the biological study regarding the activities that take place in a cell to keep it alive. This comprises animal cells, microorganisms, and plant cells . The term physiology mention to all the normal functions that take place in a living organism. The function of Cell Physiology is Organ-systems are a group of cells, tissues, and organs, which have dedicated functions in the body. Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes within the connection to living organisms. It was divided into three fields biochemical metabolism, Proteins, and molecular genetics. Biochemistry focuses on understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living between cells and cells which in turn relates greatly to the understanding and study of tissues, organisms, organ structure, and function. Foundations of cell physiology are animals, cells, plants, viruses, and microorganisms.
Track 5: Cell Cycle and Cytogenetics
The cell differentiation or cell cycle is the sequence of events that take place in a cell leading to its duplication and division of its DNA (DNA replication) to produce two daughter cells. It plays an important part in the growth of embryos, and for the development and growth of our bodies as well. Mitosis produces new cells and replaces cells that are old, damaged or lost and in mitosis, a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells. Cytogenetics is a branch of gene technology that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behavior, particularly to their behavior during meiosis and mitosis. Quinacrine banding was the first marking method used to produce specific banding patterns. This method requires a fluorescence microscope and is no anymore as widely used as Giemsa banding. The Causes of cell sorting is cancer by accelerating cell division rates or prevent normal controls on the system, such as cell cycle programmed cell death or arrest.
Track 6: Molecular Cell Biology
Molecular and cell biology is a branch of biology that reads the function and structure of the cell, which is the basic unit of life. It concerned with physiological properties and metabolic engineering. Its activity of biomolecules in the different systems of a cell, including the interactions between DNA, RNA, and proteins their biosynthesis, as well as the regulation of these interactions. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is basic to all biological sciences, it is also essential for research in biomedical fields such as cancer and other diseases. Research in cell biology is closely related to genetics, biochemistry, molecular, cytochemistry, biology and immunology. The techniques of molecular cell biology are Cloning, Polymerase chain reaction, Gel electrophoresis, Microarray, Allele-specific oligonucleotides.
Track 7: Epigenetics and Metagenomics
Epigenetics is the study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression rather than alteration of genetic codes as heritable phenotype it does not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. We produce steroid hormones called glucocorticoids that affect many systems throughout the body in during stress, behavior, physical activity, alcohol and smoking in situations. Metagenomics is a single pass tyrosine kinase receptor essential for embryonic development, organogenesis and wound healing, it is the genetic mutations recovered directly from environmental samples.I t most often indicates changes that affect gene activity and expression but can also be used to narrate any heritable phenotypic change. Such effects on physiological and cellular phenotypic traits may result from external or environmental factors.
Track 8: Structural Biology
Structural biology is a branch of biophysics, molecular system biology, and biochemistry concerned with the molecular biological macromolecules. Structural biology is important for carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids, structure and function are related in biological science because of a certain structure a living thing makes contain and the object function the way it does. The bonding of a function and structure is structuring levels from molecules to organism ensure successful functioning in all living organism and living system. Many Researchers lack the background to fully utilize the property of solved three-dimensional biology of immune system.
Track 9: Proteomics and Transcriptomics
The transcriptome is the set of all molecules of RNA analysis in one population of cells or one cells, it is used and also sometimes refers to all RNA depending on the particular experiment. Proteins are the large scale of the Proteomics and those vital parts of living organisms with many functions. The proteome is the entire set of proteins that are modified or produced by an organism or system. Proteomic technology generally refers to the large-scale experimental analysis of proteins and proteomes but is often specifically used to refer to protein mass spectrometry and purification. The proteome is the entire set of proteins that are modified or produced by an organism or system and proteomics has enabled the identification of ever increasing numbers of protein.
Track 10: Calcium and Cell Function
Calcium is a mineral that is important for life, In addition to construction bones and keeping them healthy, calcium authorize our blood to clot, our muscles to contract and our heart to beat. About 99% of the calcium in our bodies is in our bones and teeth when calcium is too low level may result from a problem with the parathyroid glands and cell culture, as well as from diet certain drugs or kidney disorders. Cell Functions are Toxic substances, contain receptors and channels that allow specific molecules, such as ions, nutrients, metabolic disorder, and wastes products also nutrients and energy. The common cause of cell death is a deficiency of oxygen and Hypoxia is extremely important.
Track 11: Structural & Functional Genomics
Structural genomics seeks to report the 3-dimensional structure of every protein encoded by given genomics. This genome-based is nearer to allows for a high-throughput method of structure determination by a compound of modeling and experimental approaches. Functional genomics is a field of Structural molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data given by genomic and transcriptomic to describe gene interaction and functions. Unlike structural genomics, functional genomics focuses on the dynamic aspects such as gene transcription, translation, protein-protein interactions and regulation of gene expression, as opposed to the static feature of the genomic information such as DNA structures or sequence.
Track 12: Cancer Genomics
Cancer genomics is the study of the entirety of gene expression and DNA Sequence differences between normal host cell and tumor cells. It's the promise of precision cancer treatment a focus on the independent tumor in the individual patient. Cancers types are including breast cancer, ovarian, colorectal, and prostate cancer as well as some other, less common, rarely certain types of cancer can be passed down through generations and environment. The symptoms of cancer may become depressed and anxious post diagnosis the risk of suicide in people with cancer is roughly double.
Track 13: Microbial Glycobiology & Genomics
Glycobiology is the study of the structure, biology and biosynthesis of saccharides that are widely distributed in nature. Saccharides or sugars are essential components of all living things and aspects of the different roles they play in biology are researched in various medical, biotechnological and biomedical fields. Microbial is the ecology protection of microorganisms their state of being connected with one another and with their environment. It concerns the three major domains of life Eukaryota, Bacteria, and Archaea as well as viruses. As a consequence of microbial genetics the relating to the magnitude of microbial life microbes, by virtue of their biomass alone, constitute a significant carbon sink, Aside from carbon fixation, microorganisms key collective metabolic control global biochemical cycling.
Track 14: Yeast Artificial Chromosome
Yeast artificial chromosomes are beginning to engineered chromosomes obtain from the DNA of the yeast and Saccharomyces cerevisiae which is then ligated into a bacterial plasmid. By placing large fragments based drug design of DNA and sequences can be cloned and physically survey using a process called chromosome walking. This is the procedure that was initially used for the Human Genetics, however,r due to stability issues, YACs were deserted for the use of Bacterial artificial chromosomes. The main components of a YAC are the ARS, telomeres, and centromere from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Additionally, selectable target genomics such as antibiotic resistance and a visible marker are utilized to select change yeast cells.
Track 15: Stem Cells & Tissue Engineering
Biological cells are called Stem cells that can differentiate into other types of cells and can divide to produce more of the same type of stem cells .They are past participle in multicellular organisms., it consists of more than one cell in contrast to unicellular organisms. Tissue culture engineering is the use of a combination of cells, materials and engineering methods and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to become better or replace biological tissues. Tissue engineering involves the use of a tissue scaffold for the being formed of new viable tissue for a medical purpose. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in importance and scope it can be considered as a field in its own. Bone marrow has been used to treat people with cancer and with conditions such as leukaemia and lymphoma, this is the only form of stem-cell therapy that is widely repeated.
Track 16: Gene expression & Genetic Changes
Gene expression is the operation by which information from a genome biology is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but ina non-protein coding gene such as the move from one place to RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA. The procedure of gene synthesis expression is used by all known life eukaryotes prokaryotes and utilized by viruses to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. Several steps in the gene technology expression process may be modulated, including the transcription, RNA splicing, post-translational and translation modification of a protein. A gene mutation is a permanent alteration in the DNA sequence that makes up a gene, such that the sequence various from what is found in most people. Mutations range in size they can make a difference to anywhere from a single DNA building block to a large segment of a chromosome that includes multiple genes.
Track 17: Plant Biology & Genomics
Plant biology is the study of genes, heredity and genetic variation specifically in Plants. These observed that organisms that cause infectious disease include plants and fungi, oomycetes, bacteria, viruses, viroid’s, virus-like organisms, phytoplasmas, protozoa, parasitic plants and nematodes inherit traits by way of discrete units of inheritance and this term still used today is a somewhat ambivalent. A plant phylogenetics gathering represents the complete plant genetics sequence of a plant species, which is gathered into chromosomes and other organelles by using DNA fragments that are obtained from various types of sequencing technology. Plants like all other known living organisms move on their traits using DNA and however are the same from other living organisms in the fact that they have Chloroplasts.
Track 18: Animal cells & Microbial Interactions
Animal cells are representative of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles and different from the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall. Microbial genetics Interaction between various microorganisms and include both positive and negative interaction, also it is an assemblage of species living close enough for potential interactions and within a community different consortia may be found. The various types of microbes in an interaction are identified and characterized by several methods. Interaction may change over time, Bioleaching and waste water treatment plants are non-sterile environments. Therefore various types of microorganisms will live common in a community, the interactions between the microbes matter much for the outcome of the processes.
Track 19: Human Genomics
Human genomics is the study of the provision as it occurs in human beings. The Human genome is the total set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome couple in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within own mitochondria. Human genomes involve both protein-coding DNA genes and noncoding DNA. Human genetics encompasses a differently of overlapping fields including classical genetics , cytogenetic, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, developmental genetics, genetic counselling and clinical Ethic genetics. Human genetic variation is the genetic differences in whole populations, there may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population, a situation called polymorphism. No two humans are genetically identical, even monozygotic twins having infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during improvement and gene copy-number variation.
Track 20: Single Cell biology
The Single cell biology is also called as a unicellular organism. It is the study of the function and structure of the cell. Single cell organisms are composed and microscopic of a single cell gene expression, unlike multicellular organisms that are made of many cells. They can carry and live out all of their life processes as one single cell. All prokaryotes, some fungi and most protists are unicellular. Some of these organisms do live in large colonies, but every individual dendrites cell biology is a simple living organism. Let's look at some examples of unicellular organisms. Valonia ventricosa is a protist, Transcriptomics and their Techniques.
Track 21: Clinical & Pharmacogenomics
Clinical pharmacology is the science of drugs and their clinical use also it is underpinned by the main science of pharmacology with an added focus on the application of pharmacological principles and quantitative methods in the real world, therefore clinical pharmacology is not specific to medicine. The purpose of pharmacogenitics analyses how the genetic makeup of an individual effects on human response to drugs. Pharmacogenomics aims to improve rational means to optimize drug therapy, with regard to the patient’s genotype to ensure maximum efficiency with minimal adverse effects.
Track 22: Population & Evolutionary Genomics
Population genetics is the study of the changes and distribution of allele frequency in a population, as the population health is subject to the four main evolutionary processes: natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow and mutation. Population genomics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic various within and between populations is a part of evolutionary biology. Population genetic models are used a couple for statistical inference from DNA sequence data. Human evolutionary genetics refers to how one human genome differs from another human genome, the evolutionary past that gave rise to it, and its current effects. Differences between genomes have anthropological, historical, forensic implications, applications and medical. Genetic data can provide mainly insight into human evolution.
Track 23: Molecular Biology & Transcriptomics
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA molecular biology in a population of cells or one cell. It vary from the exome in that it includes only those RNA molecules found in a specified cell population, and usually covers the amount or concentration of each RNA molecule in addition to the molecular identities. Transcriptome techniques comprise DNA microarrays and next-generation sequencing technologies called RNA-Seq, transcription can also be studied at the level of individual cells by single-cell transcriptome. One of the most primary techniques of molecular biology to study protein function is molecular cloning. In this technique, DNA coding for a protein of heed is cloned using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and restriction enzymes into a plasmid.
Track 24: Molecular Biology Techniques
Molecular biology techniques are familiar methods used in molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics and biophysics which mostly involve manipulation and analysis of DNA, RNA, protein, and lipid. One of the main basic techniques of molecular biology to study protein function is molecular cloning and in this technique, DNA coding for a protein of interest is cloned using polymerase chain reaction the level of molecular is very smallest units that make up organisms or elements and tests done by sample of blood, hair, skin, amniotic fluid or other tissue. Gene amplification is a methodology in which a certain gene or DNA sequence is replicated many times in a process called DNA.
Track 25: Genomic Medicine
Genomic Medicine is also known as personalized medicine, and it is a way to customize medical care to your body's common genetic makeup. Each of the cells in the body contains DNA, the molecules, you receive from your parents that determine how your body looks and functions. Each and every one responds to stress and the environment differently and they also respond to disease and to treatments differently. Although greater than 99% of a DNA sequence is identical from one person to another person, the last 1% helps to describe these differences. Various people may have small variations in specific gene expression, and some people may have genes that others don’t. These may develop susceptibility to a specific disease or provide protection from that illness. Scientists continue to discover new ways that subtle gene flow various cause large differences in health, this understanding can lead to better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat many types of health conditions.
Track 26: Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant DNA technology, relate together of DNA molecules from two various species that are inserted into a host organism to produce new genetic combinations that are of value to science, medicine, agriculture, and industry. The Processes of Recombinant gene DNA Technology is joining DNA molecules from two different interesting and sources them into a host organism, to generate products for human use. The applications of health and nutrition, in medicine it is used to create pharmaceutical products such as human insulin and In agriculture, it is used to impart approving characteristics to plant to increase their yield and improve the nutritional content of Recombinant DNA technology.
Track 27: Computational Biology & Next generation sequencing
Next Generation Sequencing is used to rule the primary structure of an unbranched biopolymer it results in a symbolic linear depiction known as a sequence which succinctly summarizes much of the atomic-level structure of the sequenced molecule. Computational molecular Biology, which comprises many aspects of bioinformatics tools, is the science of using biological data to improve modes or algorithms to understand biological systems and relationships. Next generation sequencing works by reading the nucleotide sequences at the single cell molecule level, in contrast to existing methods that need breaking long strands of DNA into small segments then inferring nucleotide sequences by synthesis and amplification.
Track 28: Data integration, Modelling and Prediction
Data integration is the procedure of combining data generated using a variety of different research various in order to enable detection of underlying themes and in Computational biology and bioinformatics, biological principles. Data Analysis in this arena is dataintensive, which means data sets are large and highly heterogeneous, to create knowledge from data, researchers must integrate these large and diverse datasets. Predictive genomics is at the intersection of multiple disciplines as predictive medicine, translational bioinformatics and personal genomics. Specifically, predictive genomics deals with the future phenotypic outcomes through prediction in areas such as complex multifactorial diseases in humans. Prediction and Modelling involves the use of computer simulations of biological systems, including cellular subsystems, such as the networks of enzymes and metabolites which comprise metabolism, signal transduction pathways and gene technology regulatory networks, to both visualize and analyze the complex connections of these cellular processes.
Cell Biology 2019
Theme: Engineering Biomolecules for Advancement of Drug Discovery and Molecular Therapeutics
ME Conferences welcomes all participants, moderators, and exhibitors from everywhere throughout the world to Helsinki, Finland. We are enchanting to invite all of you to attend the International Conference On Cell Biology and Genomics which will be held during June 10-11, 2019 in Helsinki, Finland.
Scope and Importance
Cell Biology deals with the study of the structure, function, and organization of cell and its organelles. It provides us an insight on how varied components of a cell depend upon works and one another in coordination for the optimal functioning of the body. Ranging from the terribly primitive organic structure to the range of forms present now, the Cell Biology helped us to know different forms of life. Throughout evolution, mature organic structure evolved and the details of many changes in structure and performance are studied through Molecular Cell Biology and various techniques of enclosed in biology.
Cell Biology is an extremely dynamic field of life science analysis that uses knowledge-based approaches to grasp traditional and pathological cellular processes at the molecular level. The findings of basic analysis have entered clinically, as new therapeutic and diagnostic assays ways does not focus solely on the symptoms, additionally on the causes of sickness.
Why in Helsinki, Finland?
A Unique genetic background in an isolated population like that of Finland provides for applying the genetic evolutions as well as special chances for genetic research to health care. On the other hand, the various genetic backgrounds may require local attempts to develop diagnostics and treatment as the selection of diseases and mutations differs from that in the other populations. In this review, we narrate the experiences of research and health care in this genetic isolate starting from the identification of specific monogenic diseases enriched in the Finnish population all the way to execute the knowledge of the unique genetic background to genomic medicine at the population level.
In the case of Finland, couple geographical isolation due to the very Nordic position of the country and cultural isolation due to religious and language boundaries have caused enrichment of some disease-causing gene variants and losses of others. The special genetic constitution of the Finnish population has had a profound effect on the research of genetics of common and both rare diseases as well as on some health care practices. As genomic tools will be more widely used in the healthcare in the future, the common genetic context of Finns and other isolated populations can be anticipated to offer exceptional possibilities for executing genomic medicine at the population level.
Target Audience
Cell Therapy Scientists, Researchers, and Students
Molecular Medicine Scientists, Researchers, and Students
Biotechnologists
Immunologists
Gene therapy Researchers, Scientists, and Students
Cell and Gene therapy Faculties
Cell and Gene Therapy Associations and Societies
Stem Cell Students, Scientists
Stem Cell Researchers and Faculty
Stem Cell Associations and Societies
Training Institutes
Research Scholars
Directors of Molecular Biology
Healthcare Professionals
Medicine Department Associations
Industrialists
Hospitals and Health Services
Executives/Managers and Business Delegates
Clinical Fellows
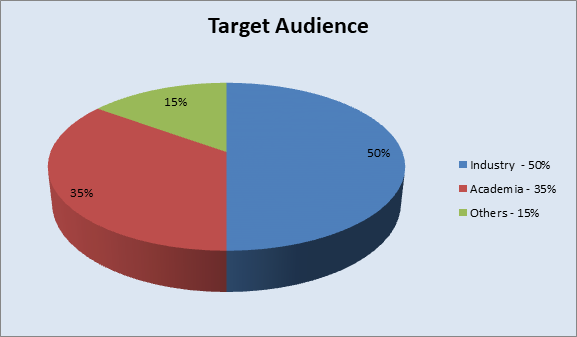
Market Research
The global cellular analysis market for cell biology tools and reagents reached $45.9 billion in 2014 and $48.2 billion in 2016. The market should reach $58.0 billion by 2020, growing at a Compound Annual Growth rate (CAGR) of 3.8% from 2015 to 2020.
The scope of this study involves the tools and reagents employed in the genomics markets. The genomic markets include both the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. The tools and reagents covered in this report are used to conduct research in the domains of genomics and cell (DNA and RNA research), proteomics, cell biology research, epigenetics, metabolomics, bioinformatics, microscopy and imaging, and stem cell research. Also included are the markets of recombinant animal models, antibodies and proteins. Introduction of technology advanced cell analysis instruments, increasing incidence of infectious and chronic diseases, a rising number of patients suffering from cancer, and increasing investments from various government life sciences & associations companies for cell biology research activities.
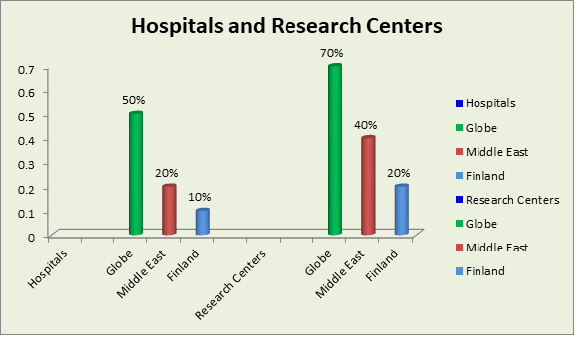
List of Hospitals and Research Centres
Worldwide
NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital
International Livestock Research Institute
Chinese National Human Genome Center
Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology
Columbus Community Hospital
National Center for Genome Resources
National Institute of Genetics
Philippine Genome Center
Genome Institute of Singapore
Middle East
Max Plank Institute for Molecular Genetics
Mediclinic Al Noor Hospital
International Genetic Resources Institute
Mediclinic Welfare Hospital
Institute of Molecular Systems Biology
Finland
Folkhalsan Research Center
The Minerva Foundation Institute for Medical Research
Helsinki Finland Hospital
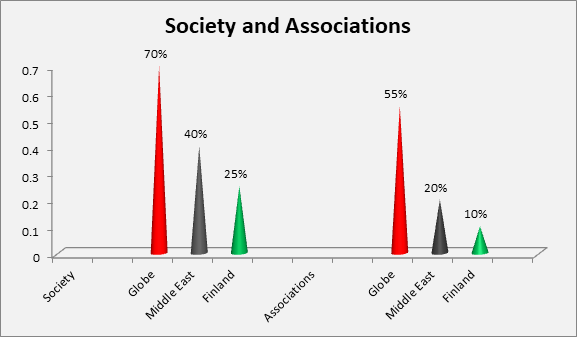
Major Associations and Societies
Worldwide
American Federation for Medical Research
The European Association of Nuclear Medicine
Association for Molecular Pathology
Chinese Society for Cell Biology
The Hong Kong Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Chinese Society for Cell Biology
Molecular Pathology Association of India
American Society of Gene Therapy
Middle East
Middle East Molecular Biology sources
European Molecular Biology Network
Emirates Medical Society
Biology Graduate Students Association
Hellenic Society for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
Israeli Society of Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
Finland
ESHG European Society of Human Genetics
EDMA European Diagnostic Manufacturers Association
FEBS Federation of European Biochemical Societies
Romanian Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
ESCV European Society for Clinical Virology
The European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM)
European Federation of Molecular Biology
European Association of Pharma Molecular Biology
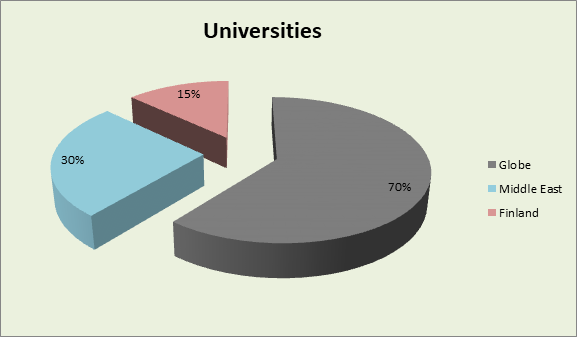
List of Universities
Worldwide
Harvad University
University of Cambridge
Standford University
University of Oxford
University of California
Yale University
The George Washington University
University of Toronto
University of Rhode
Miami University
Middle East
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
King Saud University
Cairo University
American University of Beirut
King Abdul-Aziz University
United Arab Emirates University
Alfaisal University
Mansoura University
Sultan Qaboos University
Finland
University of Helsinki
University of Eastern Finland
University of Oulu
University of Tampere
University of Turku
Projections: Growth by the next 5-10 years
In the past decade, the prospects for the future and their responses highlight the incredible changes that the field has seen, from the explosion of genomic data and the many possibilities it has been opened up to the ability to reprogramme adult cells to pluripotency. The way ahead looks similarly exciting as we address questions such as how complex interactions among genetics and cells function as systems, epigenetics, and the environment combine to shape phenotypes. Epigenetics may provide hope that we are more than just the sequence of our genes, that our children and that of our destiny can be shaped, to some extent, by our lifestyle and environment. Our grasp of the molecular basis of epigenetics has expanded well on DNA methylation, which was previously the best known epigenetic mark. It now includes other chromatin components, such as histone-histone and variants modifications, as well as associated protein complexes.
Related Societies:
United States:
- American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ASGCT)
- American Society of Gene Therapy (ASGT).
- American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB)
- The International Society for Systems Biology (TISSB)
- Colorado Bioscience Association (CBA)
- Indiana Biosciences Research Institutes (IBRI)
- American Association of Pharmaceutical Scientists (AAPS)
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHSP)
- Federation of the American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB)
Europe:
- European Tissue Repair Society (ETRS)
- European Society of Gene and Cell Therapy (ESGCT)
- European Association for Chemical Sciences (EACS)
- European Pharmaceutical Market Research Association (EPMRA)
- European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL)
- European Association of Pharma Biotechnology (EAPB)
- European Federation for Immunogenetics (EFI)
Asia-Pacific:
- The Korean Society for Molecular and Cell Biology (TKSMCB)
- The Molecular Biology Society of Japan (TMBSJ)
- The Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS)
- Chinese Pharmaceutical Association (CPA)
- The Pharmaceutical Association of Israel (TPAI)
- Kuwait Pharmaceutical Association (KPA)
- Australasian Proteomics society (APS)
Middle East:
Conference Highlights
- Human Genomics
- Structural Biology
- Cell and Immunology
- Cellular Metabolism & Signalling
- Membrane Processes
- Cell Physiology and Biochemistry
- Cell Cycle and Cytogenetics
- Molecular Cell Biology
- Epigenetics & Metagenomics
- Proteomics and Transcriptomics
- Calcium and Cell Function
- Structural & Functional Genomics
- Cancer Genomics
- Microbial Glycobiology & Genomics
- Yeast artificial Chromosome
- Stem Cells & Tissue Engineering
- Gene expression & Genetic Changes
- Plant Biology & Genomics
- Animal cells & Microbial Interactions
- Single Cell biology
- Clinical & Pharmacogenomics
- Population & Evolutionary Genomics
- Molecular Biology & Transcriptomics
- Molecular Biology Techniques
- Genomic Medicine
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Computational Biology & Next generation sequencing
- Data integration, Modelling and prediction
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 15-16, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Cell Science & Therapy
- Cell Biology: Research & Therapy
- Journal of Genetic Syndromes & Gene Therapy
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by















